Image: Shutterstock
A shellfish is an aquatic creature with an exterior that resembles a shell and lives in freshwater and saltwater. When can babies eat shellfish–is a question many parents have. Although adding shellfish to a baby’s diet might be beneficial for their health, it can also trigger allergies since they can be contaminated with hazardous materials such as cadmium and mercury.
These creatures are divided into mollusks and crustaceans and are rich in micronutrients, protein, and healthy fats, which can help support a baby’s development and growth.
In this post, we tell you about the nutritional value of shellfish, when to introduce it to your baby, how to safely consume it, and points to consider when feeding it to your baby.
When Can Babies Eat Shellfish?
Image: Shutterstock
Some experts suggest feedingwell-cooked shellfishonce the baby is older than six months and has started consuming other solids, such as cereals, grains, poultry, and meat. However, some recommend delaying it up to 9 to 12 months due to its potential to cause allergies(1).
Consult a pediatrician and know the right age to start feeding shellfish to your baby, especially if you have a family history of food allergies.
Nutritional Value Of Shellfish
The nutritional value varies across the types of shellfish (crustaceans and mollusks). The commonly consumed crustaceans are crab, crayfish, lobster, shrimp, krill, and prawn, while widely consumed mollusks are clams, scallops, oysters, and mussels(2).
Below is an approximate nutritional composition of various shellfish types (cooked) with a serving size of three ounces (85g)(3).
| Type | CALORIES (KCAL) | Protein (g) | Fat (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scallops | 140 | 27 | 1 |
| Shrimp | 100 | 21 | 1.5 |
| Blue crab | 100 | 20 | 1 |
| Lobster | 80 | 17 | 0.5 |
| Clams | 110 | 17 | 1.5 |
| Oysters | 100 | 10 | 4 |
Source:FDA
Possible Health Benefits Of Shellfish For Babies And Toddlers
Different shellfish have different health benefits. Some of the common ones are:
- Rich in high-quality protein:Shellfish like scallops, shrimp, and blue crab contain protein.Seafood protein is also a good source of digestible proteins, essential amino acids that are important for thedevelopment of babies(4).
Image: Shutterstock
- 丰富的微量元素:Moderate consumption of shellfish can supply vitamins and minerals, such as vitamins B12 and D, sodium, potassium, copper, zinc, and iodine(2). These micronutrients help regulate several essential physiological functions, like physical and mental growth.
- Source ofhealthy fats:Polyunsaturated fatty acids (good fats), such as DHA and EPA, which are types of omega-3 fatty acids(2), are present in good amounts in shellfish. These nutrients help in the brain heart and brain development.
- Immunostimulating properties:Shellfish contain carotenoids like astaxanthin, which has immunostimulating properties(2). It also has peptides, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A, D, B12, iron, copper, and zinc, which are considered beneficial for the immune system(5). Thus, regular consumption of shellfish may help boost immunity in the long run.
Image: Shutterstock
Regular consumption of shellfish may have cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral benefits, as well.
Possible Side Effects Of Shellfish In Infants
Image: Shutterstock
Just like any other food, shellfish has its share of potential side effects for babies.
- Foodborne illnesses: Raw and undercooked shellfish, mostly clams, oysters, and mussels, may contain viruses and bacteria that can lead to poisoning. Shellfish from contaminated water can contain dangerous pathogens, such as norovirus(6). Besides, contaminated shellfish may contain marine contaminants, such as harmful algal bloom (HAB) toxin and brevetoxin, which might be fatal for babies(7)(8).
- Chemical contamination:Lobsters, scallops, and crab can be prone to mercury contamination(9). Other shellfish can also be contaminated with lead and mercury, especially when harvested from polluted waters. High levels of mercury can adversely affect the central nervous system(10).
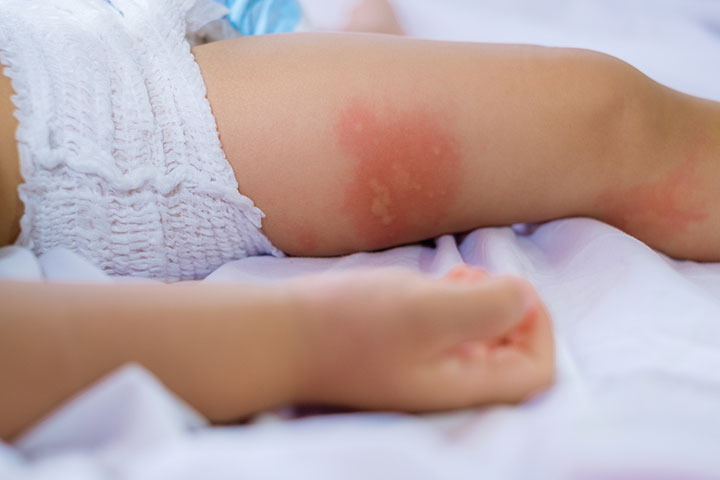
- Allergy:The allergic reaction to shellfish depends on the individual and the type of shellfish. Some of the commonfood allergysymptoms are wheezing, trouble breathing, coughing, diarrhea, stomach ache, red spots, hives, and itchy, watery, swollen eyes. An extreme allergic reaction can cause anaphylaxis(11).
 Quick fact
Quick factSee a doctor promptly if you notice any allergy symptoms or if your baby seems unwell after consuming shellfish.
The best way to avoid these adverse effects is to follow FDA guidelines and advisories on fish and shellfish selection, storage, and cooking.
Tips To Include Shellfish In Your Baby’s Diet
Image: Shutterstock
Here are some suggestions that may help in the safe introduction of shellfish to babies, minimizing its potential adverse effects.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends serving an ounce (30g) of fish and shellfish, once or twice a week, to toddlers between two and three years of age(12). However, there are no clear recommendations available for babies. When introducing a new food, start with a small amount to minimize a potential allergic reaction. Therefore, consult your pediatrician on the right amount of shellfish consumption for your baby.
- Purchase shellfish from trusted sellers, preferably those approved by the government or the FDA. It can ensure shellfish’s freshness and that it does not contain any contaminants, such as mercury, or has it within the safe limits of human consumption.
- Never feed uncooked or under-cooked shellfish to a baby as it can increase the risk of food poisoning(13). The CDC states that seafood should be cooked to at least 145°F (63°C).
- Cook shellfish at home and do not feed shellfish bought from a restaurant. Do not feed any leftover cooked seafood to a baby. Cross-contamination from cooking utensils or cooks touching different foods occurs easily in restaurants. So ensure to maintain optimum hygiene during food handling and preparation.
- Introduce only one type of shellfish at a time. Follow a “three-to-five day wait” rule to check for allergic reactions.
- Feed small amounts, like half to one teaspoon at a time. It could help your baby to adjust to the taste, texture, and digestion of the food.
- Babies below the age of 12 months should be fed shellfish as puree, paste, or a mash. Toddlers over the age of 12 months can be served well-cooked small pieces of shellfish asfinger food.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s the difference between fish and shellfish?
简而言之,these aquatic animals are differentiated by the presence of gills, backbones, and fins in fish, whereas shellfish are marine invertebrates with exoskeleton features.
2. Is shellfish a choking hazard for my baby?
是的,贝类对b是一个潜在的令人窒息的危险abies due to its chewy, rubbery texture and round shape. Make sure to chop them into small pieces before serving them to your children.
3. Can babies outgrow shellfish allergy?
Yes, about one-third of the babies eventually outgrow their shellfish allergy. An oral food challenge test by an expert can determine if the patient has outgrown their allergy(14).
4. Does Benadryl help with a shellfish allergy?
Benadryl is an antihistamine and a sedative used in mild cases of food allergy. However, in case of severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis, Epinephrine is the first line of treatment before calling 911(14).
When can babies eat shellfish–you may introduce it along with other solid foods by six months, but it may be safer to start them by 12 months as the harmful effects of allergies, if triggered, may be lesser by that age. Start with small portions of well-cooked shellfish and gradually include them as a part of a balanced diet for your baby. Shellfishes are good sources of proteins, micronutrients, and omega-3 fatty acids that may protect against inflammation and viral infections. Exercise caution while selecting, storing, and cooking shellfish to avoid contaminants and the risk of food poisoning.
Infographic: Tips To Include Shellfish In Your Baby’s Diet
As your baby grows and starts to eat solid foods, it can be a great idea to introduce shellfish into their diet. However, it’s important to avoid raw shellfish, as it can carry bacteria or other contaminants. The infographic below presents tips on feeding shellfish to your little one. Read on!

Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Get high-quality PDF version by clicking below.
Download Infographic
Key Takeaways
- Babies can have shellfish once they start with solid foods, within six to 12 months of age.
- Shellfish are a good source of protein, boost immunity, and contain essential micronutrients.
- You can include shellfish in your baby’s diet about once or twice a week.
- Overconsumption of shellfish by babies might put them at risk of allergies and food borne illnesses.
Explore the numerous benefits of shellfish and how they can improve your health and nutrition. Learn why shellfish can be a great addition to your diet.
References:
2. VazhiyilVenugopal and KumarapanickerGopakumar;Shellfish: Nutritive Value, Health Benefits, and Consumer Safety; Wiley Online Library
3.Seafood Nutrition Facts; U.S. Food And Drug Administration.
4. RyotaHosomi et al.,Seafood Consumption and Components for Health; CCSE
5. Faye M. Dong,The Nutritional Value of Shellfish; University of Washington
6.Foods That Can Cause Food Poisoning; CDC
7.Marine Environments; CDC
8.Case Definition: Brevetoxin; CDC
9.All About Shellfish; Winchester Hospital
10.EPA-FDA Advice about Eating Fish and Shellfish; EPA
11. Shellfish Allergy; John Hopkins All Children’s Hospital
12.Healthy Fish Choices for Kids; Healthy Children; AAP
13.Foods to avoid giving babies and young children; NHS
14.Shellfish
15. Aaron S. Bernstein, et al.;Fish, Shellfish, and Children’s Health: An Assessment of Benefits, Risks, and Sustainability; National Library of Medicine
16.Shellfish; American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology