Image: iStock
During pregnancy, your blood volume increases by up to 50%.With a decline inhemoglobinlevels andhematocritiXThe percentage of red blood cells (RBCs) in blood(particularly in the last trimester), theplatelet countalso slightly decreases.However, the white blood cells (WBCs) in the blood increase following pregnancy, termed leukocytosis.
Leukocytes or WBCs are classified as agranulocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes) and granulocytes (eosinophils, neutrophils, and basophils), which make up the body’s immune system and fight against infection (1).
Read this post to know about the causes of high WBC count in pregnancy and the complications associated with this condition.
What Is The White Blood Cell Count During Pregnancy?
Image: IStock
Following pregnancy, there is a gradual increase in the normal WBC count (leukocytosis), with a slight shift toward an increased percentage of neutrophils.
Leukocytosis begins in the firsttrimester, continues throughout the pregnancy, peaks during delivery, and usually normalizes after four weeks (1) (2).
| Trimesters | WBC (Leukocyte) count |
| Non-pregnant reference range | 4.8–10.8 x 103/mm3 |
| First and second trimesters | 6–16 x 103/mm3(3.5 x 103/mm3increase) |
| Third trimester | 20–30 x 103/mm3 |
However, several studies have associated leukocytosis in the first trimester with a complicated pregnancy,preeclampsiaiXA pregnancy condition characterized by the onset of high blood pressure, protein in the urine, and water retention, andgestational diabetes mellitusiXA condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to hormonal and physical changes in pregnancy
(GDM) (3) (4). Therefore, the leukocyte count must be correctly interpreted and correlated during your antenatal visits and postnatal care (1).
During pregnancy, the white blood cells are frequently examined to look for signs of infection or inflammation in the body. The WBC levels rise from eight to forty weeks into the gestational period. As seen in the graph below, they peak around the 32nd week and start sloping downward (12).
白细胞在怀孕
Source:White Blood Cells in PregnancyWhat Are The Causes of High WBC Count During Pregnancy?
Liesel Teen, BSN, a registered labor and delivery nurse from Raleigh, North Carolina, says, “Even in healthy pregnancies, it is normal for a woman’s WBC count to increase, especially towards the end of pregnancy. However, if this elevation is accompanied by any signs of infection or other medical conditions, it likely will warrant further testing and evaluation.
“Specific causes of elevated WBC counts include bacterial or viral infections, leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, certain medications (such asepinephrineiXA hormone as well as a neurotransmitter responsible for the body’s fight or flight responseor corticosteroids), severe allergic reactions, and even severe stress. Any bacterial or viral infection in the body can result in an elevation in a person’s white blood cell count.”
In general, an increased WBC count indicates (1)
- Acute infection
- Trauma
- Dehydration
Image: IStock
- HemoconcentrationiXAn increase in the cellular components and a decrease in plasma volume in the blood
- Cancer (such as chronic leukemia)
- Overuse of medications such ascorticosteroids
However, due to the physiological stress caused by pregnancy, you may have a higher WBC count even in normal pregnancy. Hence, maternal WBC count cannot be a primary screening technique for detecting severe pregnancy complications (5).Conversely, an increased WBC count in your urine sample indicates aurinary tractinfection(UTI) (6).
Image: IStock
怀孕需要一个复杂的生理反应where the内分泌系统iXA complex system of glands and organs that produce hormones, metabolic processes, and genital system undergo several changes to nourish the developing fetus and prepare the body for labor and delivery. As your pregnancy progresses, this physiological and emotional stress raises your leukocyte count as the leukocytes accept stimulatory impulses (7).
What Does The White Blood Cell Differential Count Indicate In Pregnancy?
During a healthy pregnancy, leukocytosis is generally referred to as an increased percentage of neutrophils in the blood. However, there are many types of WBCs, and elevated levels of other WBCs may imply different diagnoses (1) (8).
- Neutrophils:An increased level of neutrophils (neutrophilia) generally indicates acute bacterial infection, burns, acute stress, leukemia (blood cancer), rheumatoid arthritis, and steroid use.However, neutrophilia is normal during pregnancy due to impaired neutrophil apoptosis and may not have any clinical significance.
 Quick fact
Quick fact- Eosinophils:Eosinophilia (high eosinophil count) usually indicates the presence of allergic conditions, parasitic infections, and leukemia polyarteritis nodosa autoimmune disease. However, it also decreases with gestational age (mostly in the third trimester).
- Basophils:Basophilia (high basophil count) is generally caused by allergic conditions, chronic myelogenous leukemia, Hodgkin’s disease, and oral contraceptive usage. However, it also decreases as your gestation advances.
- Monocytes:Monocytes are the largest WBCs, and monocytosis (high monocyte count) is generally caused by chronic inflammation, Cushing’s syndrome, viral infection, and bacterial infections such as tuberculosis. During pregnancy, there is an absolute monocytosis, especially in the first trimester, but this reduces as your gestation advances.
- Lymphocytes:Lymphocytosis (high lymphocyte count) is generally caused by viral infections, leukemias, and adrenal insufficiency. However, an increase in the lymphocyte percentage in the WBCs during pregnancy may indicate a bacterial infection.
 Quick fact
Quick factHow To Diagnose High White Blood Cell Count During Pregnancy?
Image: IStock
Routine blood tests during pregnancy, such as a complete blood count (CBC) test, typically measure the leukocyte count.Your doctor may carry out diagnostic tests for hemoglobin, WBC, and platelet counts in almost every prenatal care visit to look for conditions that may complicate the pregnancy (6).
What Are The Signs Of High White Blood Cell Count During Pregnancy?
Image: IStock
An elevated white blood cell count may not present any symptoms in pregnancy. However, the symptoms of a high WBC count in non-pregnant people usually include (9)
- Fever
- Bruising/bleeding tendency
- Fatigue
- ImmunosuppressioniXA reduction in the efficacy or strength of the immune system
- Night sweats
- Weightloss
If you detect any of these symptoms while pregnant, contact your healthcare provider, as it may be a sign of infection or underlying medical complications.
Can A High White Blood Cell Count Cause Miscarriage?
While leukocytosis is common during pregnancy, it could also result from an underlying problem that typical prenatal WBC count tests cannot detect, necessitating extra screening. In the first trimester, higher platelet levels and WBC counts are linked to a higher risk ofmiscarriage, thus highlighting the significance of monitoring these markers for potential pregnancy complications (5) (10).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can preeclampsia cause a high white blood cell count?
Yes. Studies have revealed that preeclampsia can lead to an elevation in white blood cell levels (3).
2.怀孕表明白血病白细胞计数?
A blood count falling in the range of 100,000 – 400,000 indicates the presence of leukemia (11).
3. How does a high WBC count affect the immune system during pregnancy?
A high WBC count during pregnancy, also known as leucocytosis, is induced by the physiological stress of pregnancy. A moderate increase in WBC count during pregnancy is normal. However, if the WBC count rises abnormally, it may indicate an underlying condition or infection (8).
4. What precautions can be taken to prevent a high WBC count in pregnancy?
Routine blood tests conducted by healthcare providers throughout pregnancy help monitor any potential abnormalities and ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby. However, you may take general precautions, such as maintaining hygiene, staying hydrated, eating a well-balanced diet, and religiously following prescribed medications, to minimize the risk of infections and inflammatory conditions (13).
Although there could be no characteristic signs to depict a high WBC count in pregnancy, some women could experience a tendency to bleed easily, high fever, tiredness, and weight loss. In addition, during pregnancy, there may be an increase in the white blood cell (WBC) count that begins as early as the first trimester. This is due to the sudden pregnancy-related changes that occur in the body. While a slight increase in WBC count could be expected during pregnancy, it might sometimes be a sign of infections, dehydration, or other medical problems. Therefore, it is ideal to seek medical attention if you experience any atypical symptoms when pregnant to prevent adversities that could impact maternal well-being.
Infographic: Significance Of Increased White Blood Cell Differential Count In Pregnancy
One of the hematological parameters during pregnancy is an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count (leukocytosis), which is typically normal. However, some underlying problems may also increase WBC count during pregnancy. The infographic below covers the implications of the increase in different white blood cells during pregnancy.
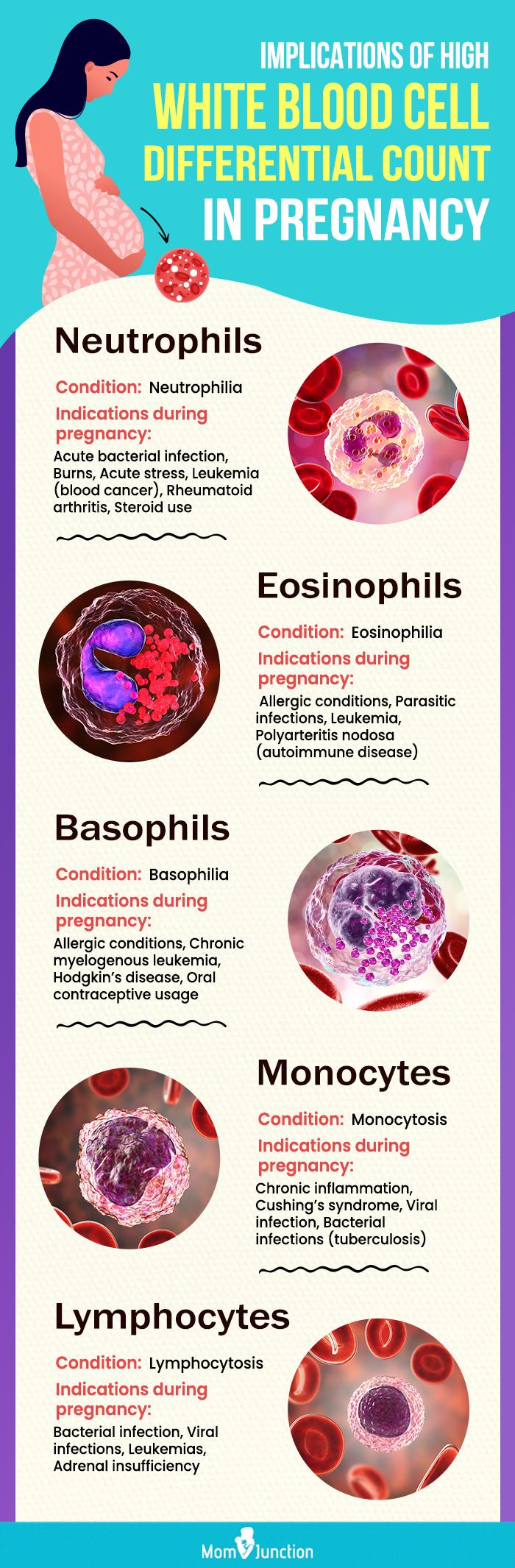
Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Get high-quality PDF version by clicking below.
Download Infographic
Key Pointers
- Increase in white blood cell (WBC) count during pregnancy might indicate several underlying conditions.
- Stress, dehydration, high blood pressure, gestational diabetes, and infections are common reasons behind a rise in WBCs during pregnancy.
- WBC or leukocyte count is a part of CBC (complete blood count), a routine serological test in pregnancy.
- It is necessary to get assessed by your physician to get an accurate interpretation and management of this condition to avoid potential complications.
Learn about the symptoms of an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count and effective management techniques. Get the answers you need to stay healthy during pregnancy.
References:
-
- David Nzioka Mutua et al.; (2018); Hematological Profile of Normal Pregnant Women.
https://www.hilarispublisher.com/open-access/hematological-profile-of-normal-pregnant-women-2165-7831-1000220.pdf - Pregnancy: laboratory measurements.
https://www.openanesthesia.org/pregnancy_laboratory_measurements/ - Bernard J. Canzoneri et al.; (2011); Increased Neutrophil Numbers Account for Leukocytosis in Women with Preeclampsia.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3062252/ - Tiange Sun et al.; (2020); Elevated First-Trimester Neutrophil Count Is Closely Associated With the Development of Maternal Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes.
https://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/69/7/1401 - Ivana Musilova et al.; (2017); Maternal white blood cell count cannot identify the presence of microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity or intra-amniotic inflammation in women with preterm prelabor rupture of membranes.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5726631/ - Routine Tests During Pregnancy.
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/routine-tests-during-pregnancy - Priya Soma-Pillay et al.; (2016); Physiological changes in pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4928162/ - Surabhi Chandra et al.; (2012); Physiological Changes in Hematological Parameters During Pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3422383/ - Lyrad K. Riley and Jedda Rupert; (2015); Evaluation of Patients with Leukocytosis.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2015/1201/p1004.html - Naser Al-Husban et al.; (2019); Platelet and White Blood Cell (WBC) Counts in the First Trimester and Pregnancy Outcome: Prospective Controlled Study.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs40556-019-00202-0 - How Fast Does Leukemia Develop?
https://www.roswellpark.org/cancertalk/201810/how-fast-does-leukemia-develop - White Blood Cells In Pregnancy : Reference Intervals For Before and After Delivery.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/ebiom/article/PIIS2352-3964(21)00509-0/fulltext - High White Blood Cell Count
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/17704-high-white-blood-cell-count
- David Nzioka Mutua et al.; (2018); Hematological Profile of Normal Pregnant Women.