Image: Shutterstock
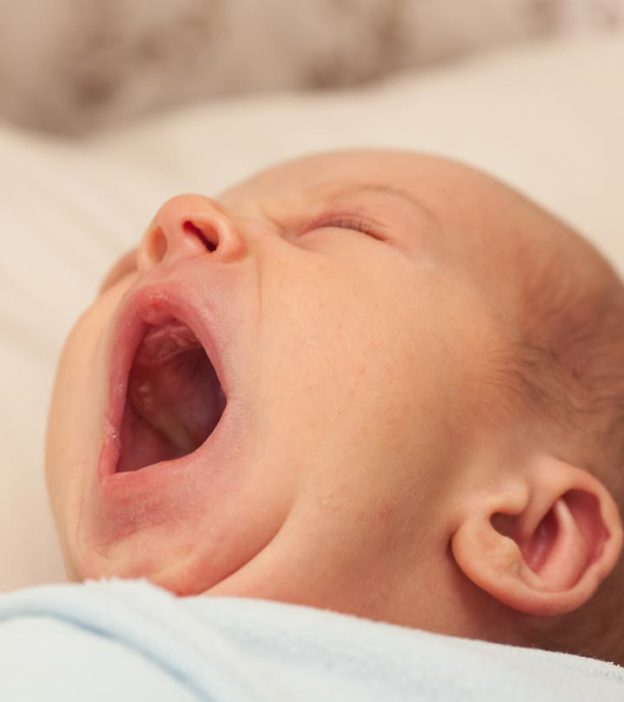
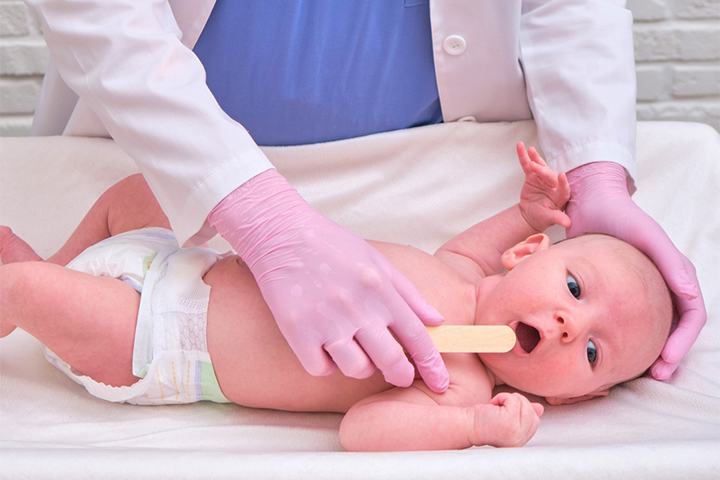
It is common to find Epstein pearls in newborn babies. They are tiny, white bumps that appear in the baby’s mouth and are also calledgingivaliXA structure consisting of gums and a mucosal layer that surrounds and protects teethcystsiXFluid-filled, benign growths that form on or under the skim. Epstein pearls have been named after Alois Epstein, a Czech pediatric physician who first described this cyst.
Approximately 60–85% of newborns have gingival cysts (1).尽管爱泼斯坦珍珠通常发现the roof of the mouth or gums in most babies, some male newborns may have it on their penis. No specific treatment is required for Epstein pearls. However, seek medical care to rule out conditions that may resemble Epstein pearls.
Read on to know the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of Epstein pearls in newborn babies.
Causes Of Epstein Pearls In Babies
Some studies suggest that Epstein pearls occur due to epithelial cells’ entrapment during palate development(1). It means that the skin gets trapped while mouth structures are developing during the fetal period. While the jaw and the palate (roof ofthe mouth) fuse during the final phase of mouth development, the skin layer may get stuck and cause tiny cysts or lesions.
Epstein pearls contain keratin, a protein found in skin and mucous membranes.
Symptoms And Signs Of Epstein Pearls In Babies
Image: Shutterstock
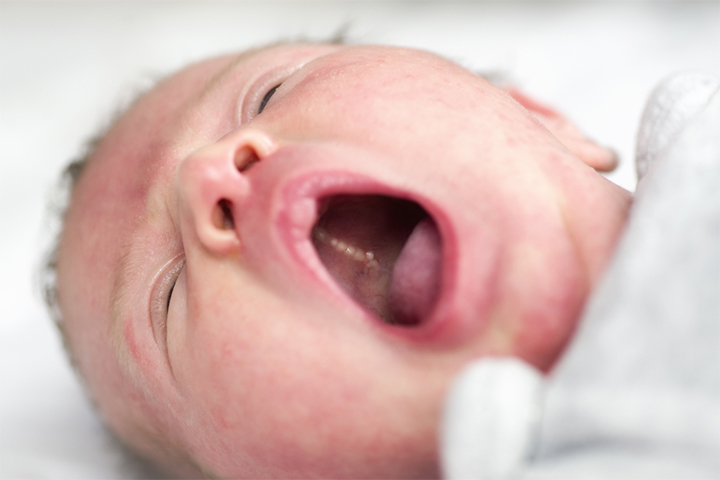
Epstein pearls appear as whitish-yellow bumps or nodules.A cyst can be one to three millimeters in size and is usually seen onthe gumsand roof of the oral cavity(1). You may notice a cluster of small round or oval bumps rather than a single bump in most cases.
They do not cause any specific symptoms, such as fever and swelling. Although Epstein pearl may resemble an emerging tooth, the cyst does not cause pain or otherteething signs.
Seek medical care if bumps do not disappear within a few weeks, bleed, or grow large in size. You may also consult a pediatrician if your infant shows signs of pain, such as refusing to feed or crying.
Are Epstein Pearls In Newborns Dangerous?
Epstein pearls are not dangerous or painful. They are benign and go away in one to two weeks(2). Cysts may often break due to friction from breastfeeding, feeding bottles, or pacifiers.
Popping or squeezing cysts may result inbacterial infectionsand increase the risk of complications, such assepsisiXA serious condition occurring as a result of an extreme reaction to an infection present in the body.
Usually, these are self-resolving cysts that go away without leaving any scars. It is rare to find Epstein pearls in babies older than three months. However, the cystic epithelium may remain in adult gingiva in some cases.
Diagnosis Of Epstein Pearls In Babies
Image: Shutterstock
A pediatrician can diagnose Epstein pearls during an oral physical examination. Laboratory examinations and imaging tests are usually not required.
An expert’s evaluation can help rule out conditions that could mimic Epstein pearls, such asoral thrushiXA fungal infection of the oral cavity that causes painful lesions, leading to eating and swallowing difficulties in babies,miliaiXSmall whitish bumps appearing on a baby’s face that are usually self-resolving, Bohn nodules (mucosal gland cysts),dental laminaiXA layer of epithelial tissue of the developing tooth, and natal teeth (teeth present at birth).
Natal teeth may irritate the baby while nursing, and some infants may accidentally swallow a fallen natal tooth. Therefore, if you notice a cyst in a baby’s mouth, consult a pediatrician to rule out the possibility of other conditions, which may cause complications.
Treatment Of Epstein Pearls In Babies
Epstein pearls may not require specific treatment and usually disappear within a few weeks(3). They may dissolve due to friction with the nipples while breastfeeding or drinking from a bottle.
奶嘴的使用和咀嚼玩具也正好ak the Epstein pearls and gradually dissolve the bump. However, it is not recommended to squeeze or pop the Epstein pearls using fingers or any other instrument.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are Epstein pearls contagious in newborns?
No, Epstein pearls are not contagious.
2. How can Epstein pearls be prevented in newborns?
There are no documented ways to prevent Epstein pearls in newborns
3. Are Epstein pearls more common in male or female newborns?
A small study with 1000 babies reports Epstein pearls to be slightly more prevalent in males than females (4).
4. Are Epstein pearls hereditary?
The condition is not known to be hereditary.
Epstein pearls in newborn babies are quite common, and they eventually disappear with time. It is advised that you consult a skin specialist or a pediatrician if the symptoms of Epstein pearls do not reduce and instead show signs of bleeding or get bigger in size. It is important to ensure that the baby does not scratch or pop the cysts as it might increase the chances of infection. Although no specific treatment is required for the treatment of Epstein pearls, it is advised that you take proper care of your baby and support the use of pacifiers as they will help dissolve the pearls.
Infographic: Some More Facts About Epstein Pearls
Epstein pearls self-resolve and do not cause any complications for most babies. If your baby has Epstein pearls, refer to this infographic to know more about their appearance and risk factors.

Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Get high-quality PDF version by clicking below.
Download Infographic
Key Pointers
- Entrapment of epithelial cells under the skin during palate development may cause Epstein pearls or white bumps in the oral cavity.
- Epstein pearls are not harmful or painful, and they often disappear within a week or two.
- You should not pop or squeeze Epstein pearls, and no specific medications are needed.
References:
2.Epstein pearls; University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
3.Epstein Pearls; MedlinePlus; United States National Library of Medicine
4. Farhana Tahseen et al.; (2014);A Cross-Sectional Prospective Study of Cutaneous Lesions in Newborn; International Scholarly Research Notices